What is Strong Customer Authentication?
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) ensures that electronic payments are performed with multi-factor authentication, to increase the security of electronic payments. It requires cardholder data from at least two of the following categories to be provided during the authentication process:

Something you know
Something only the customer knows:
- Password
- Pin
- Secret fact
Something you own
Something only the customer owns:
- Mobile phone
- Wearable device
- Token

Something you are
Something only the customer is:
- Fingerprint
- Facial feature
- Voice pattern
SCA Frequently Asked Questions
Is SCA mandatory for all transactions?
SCA is mandatory for all e-Commerce transactions although there are a number of exclusions (out of scope transactions which do not require SCA) and SCA exemptions which can be requested.
Even if a merchant flags a transaction as exempt, the Issuer still has the final say and may require the transaction to be authenticated. This is called a ‘step up’ and requires additional cardholder data to be provided so that SCA can be performed.
Do I have to implement and activate SCA Exemptions before the SCA enforcement date?
No. The use of SCA Exemptions is optional. The EVO recommended default is to use SCA as it will reduce the chance of Issuers stepping up or declining transactions that may have been sent without SCA in the early days of SCA adoption across the UK eCommerce landscape.
What are the benefits of 3DS2?
3DS2 reduces the risk of fraud and makes payments more secure as businesses and their payment provider are submitting additional data in each transaction to the cardholder’s bank (the Issuer). It allows frictionless processing through use of exemptions, although the Issuer may still require SCA. Overall it enables a better customer experience regardless of payment device type / payment channel. Further information on the expected benefits include:-
- Increased consumer confidence in an e-Commerce environment, resulting in a greater number of consumers buying on-line.
- Reduced fraud and chargebacks, with fraud-related liability protection for merchants, when SCA is applied to a transaction.
- Reduced abandonment rates due to a better user experience as the enhanced data flows will allow better decision making on a transaction and therefore potentially less challenge.
Out of scope: Which transactions are out of scope for SCA (exclusions)?
- ‘One Leg out’ (OLO) transactions
Transactions where the Payment Service Provider (PSP) of either the payer (i.e. the Issuer) or of the payee (i.e. the Acquirer) are located outside of the EEA.
- Mail Order/Telephone Order (MOTO) including Virtual Terminal (VT)
MOTO transactions are not considered to be electronic payments, and therefore are out of scope of the regulation.
- Merchant Initiated Transactions (MITs)
A series of payments with a fixed or variable amounts that the merchants performs without direct involvement of the cardholder e.g. subscriptions.
- Anonymous Cards
e.g. anonymous prepaid card.
For out of scope transactions, Acquirers and Issuers may still decide to apply SCA to the transaction, and the final decision is taken by the Issuer.
Exemptions: Which transactions may be exempt from SCA?
- SCA is mandatory for all in scope transactions however based on the risk, amount and payment channel, Acquirers and issuing banks may request / apply certain SCA exemptions to balance payment experience convenience and fraud reduction.
- Low value transactions < €30 – Issuers will monitor these transactions and SCA will be required once the total value exceeds €100 and for every 5 transactions.
- Low risk transactions – Transactions determined to be low risk by the Acquirer (or card Issuer). There are 3 transaction value bands which may qualify for this exemption, dependent on the Acquirer fraud rate).
- Recurring transactions with a fixed amount will be exempt although the first transaction requires SCA (see also Merchant Initiated Transactions below which are out of scope).
- Trusted beneficiaries (white listed merchants) – Issuers may provide cardholders with the option to assign businesses to a “whitelist” so that customers who shop with these business on a regular basis do not need SCA.
- Secure Corporate Payments B2B payments (between two businesses) using dedicated payment instruments designed for this purpose.
For all exemptions, the Issuer makes the final decision. Therefore, if the Acquirer/ merchant requests an exemption, the final decision is taken by the Issuer who may require the transaction to be authenticated. Notably the entity [merchant (via Acquirer) or Issuer] that requests the SCA exemption bears the fraud liability risk. More detail on the exemptions is listed in the table below.
How can I as a merchant request an exemption?
Please refer to the exemptions table below and the supporting materials which describe the changes required.
Table of Exemptions and Exclusions with descriptions and merchant action
| Exemption | Description | What action is needed by merchant | ||||||||
| Low value | Remote transactions up to and including 30 EUR may receive an SCA exemption; however this exemption is limited to a maximum of 5 consecutive transactions, or a cumulative limit of 100 EUR. | Merchants may need to make changes depending on e-Commerce product type and integration method (see your relevant implementation guide).
Only the Issuer can determine when the transaction counter or cumulative limit is reached and (if yes) will request authentication. |
||||||||
| Transaction Risk Analysis (TRA) | The TRA exemption allows for certain remote transactions to be exempted from SCA subject to a real-time risk check and depending on the transaction value and Acquirer’s fraud rate. It is therefore also referred as the “low risk” exemption. TRA is key to delivering frictionless payment experiences for low-risk remote transactions. Issuers and Acquirers can both apply the TRA exemption if they meet certain requirements, including achieving fraud rates according to the thresholds below:
|
This exemption relies heavily on the data provided for a transaction, so that the Issuer / Acquirer can assess the risk of a transaction. Therefore, it is highly recommended to provide all the information on a transaction as well as the cardholder. The information you as a merchant or your PSP has to provide depends on your integration method. This is explained in the relevant guide from EVO or your 3rd party gateway provider.
EVO is planning to offer this Acquirer exemption type from April 2022 on the EVO Gateway. A further communication will be issued once this is available. |
||||||||
| Recurring Transactions | Applicable when the customer makes a series of recurring payments for the same amount, to the same business. SCA is required for the customer’s first payment – subsequent charges however may be exempted from SCA.
Note: Visa does not consider recurring payments an exemption as they are part of their MIT network and thus in their opinion they are out of scope of SCA. |
The transactions must be flagged as a recurring transaction according to your PSP’s specifications in order to qualify for an exemption application. You also need to provide the transaction identifier of the first payment. | ||||||||
| Mastercard: White Listing
Visa: Trusted Beneficiaries |
Cardholders may add a merchant to a list of whitelisted/trusted beneficiaries held by their Issuer. Subsequent payments to such merchants do not require SCA. | This is primarily an Issuer exemption as the information needed is stored by the Issuer. The flagging of the granted Issuer exemption in the authorisation is managed by your PSP – no action needed.
|
||||||||
| Secure corporate payments | Payments made through dedicated corporate processes and protocols (e.g. lodge cards, central travel accounts and virtual cards) which are initiated by business entities, not available to consumers and which already offer high levels of protection from fraud may be exempted from SCA, subject to the view of the relevant competent authorities.
Lodge Cards, Central Travel Accounts and Virtual Cards that are not associated with an individual cardholder and are used within a secure dedicated corporate payment process are examples that may fall into this category. |
This is primarily an Issuer exemption as the needed information is stored by the Issuer. The flagging of the granted Issuer exemption in the authorization is managed by your PSP – no action needed. | ||||||||
| Exclusion / Out of Scope type | Use Case – Description. | Note: Merchants must ensure that transactions are coded, flagged or validated correctly for all out of scope payment scenarios to ensure correct treatment and processing. | ||||||||
| Anonymous prepaid cards | Due to their very nature, payments made with payment instruments, such as anonymous prepaid (e.g. gift) cards, are not subject to the obligation of strong customer authentication.
The Issuer is the only one able to identify this type of card. The Acquirer will not be able to identify from the primary account number that the product is an anonymous product. |
Managed by card Issuer – no action needed. | ||||||||
| Mail Order / Telephone Order – MOTO
|
Payments transacted by email or telephone are not considered to be electronic payments, and are deemed out of scope for SCA.
|
Ensure your MOTO transactions are correctly coded for all cardholder purchase / payment scenarios. | ||||||||
| “One-leg” transaction | SCA regulations apply only to transactions made entirely within the EEA. If Issuer or Acquirer is domiciled outside the EEA (“One-leg out”), no SCA mandates apply. The nationality of the cardholder nor the merchant’s business location are relevant for the assessment as to whether a transaction is out of scope due to the “one-leg” rule. EVO Risk policy and systems can influence if SCA should be applied in such instances. | Managed by your PSP – no action needed. Issuers and Acquirers may still require SCA to be applied to one-leg transactions. EVO’s current policy will require SCA for one-leg transactions.
|
||||||||
| Merchant initiated transactions – MIT
|
SCA is required for the customer’s first payment where the cardholder agrees to the terms and conditions of later subsequent charges. These subsequent charges however are excluded from SCA, provided that the cardholder is not present in the check-out flow (sometimes referred to as off-session) at the time when the charge occurs. This category also includes subsequent recurring payments. | The transactions must be flagged as a Recurring or MIT according to your PSPs specifications/ MIT framework in order to be approved by the Issuer’s as not requiring SCA. You also need to provide the ID of the first (Cardholder initiated & SCA authenticated) payment. |
How do SCA exemptions and exclusions (out of scope transactions) differ?
An SCA exemption means that the merchant / Acquirer requests an exemption (aiming to achieve a frictionless transaction without SCA) and the Issuer then decides whether SCA is required. If yes, the Issuer will trigger the authentication (challenge request) flow to authenticate the cardholder. An exclusion (“out of scope” transaction) does not require SCA / authentication obligation, provided it is flagged correctly.
Does SCA apply to transactions taken over the telephone?
No. Mail order and telephone order (MOTO) / Virtual Terminal (VT) transactions are out of scope for SCA, as they are not considered to be electronic payments. Merchants should continue to process these as they do today.
What impact does SCA have on liability for e-Commerce fraud-related disputes?
When SCA is applied to a transaction, merchants/ acquirers avail of protection in the event that a fraud-related dispute occurs. When SCA is not applied and the transaction results in a fraud related dispute, the merchant/acquirer is liable for the fraudulent transaction.
Please note: 3DS protects against fraud related disputes. It does not protect against all chargeback disputes i.e. non-fraud related disputes such as goods / services not being as described or non-delivery related disputes.
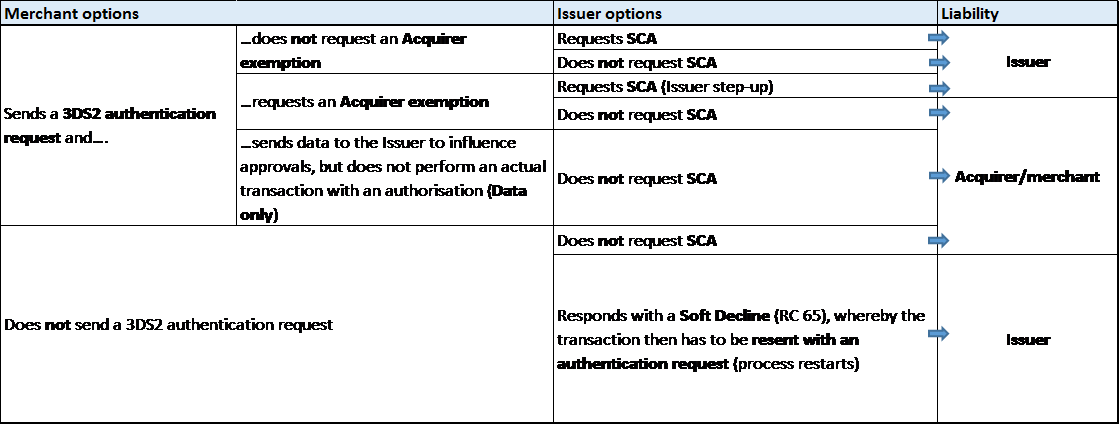
The following diagram shows the merchant and Issuer options and merchant-Issuer liability for each options
What exemptions are available at EVO Payments?
EVO will support all Acquirer exemptions subject to relevant risk policies and assessments e.g. for the local market, specific business types, individual merchant risk as applicable. EVO will be supporting the TRA exemption in 2022 for approved merchants and will advise you when this becomes available.
Does the fraud rate for the TRA exemptions apply to me as a merchant?
No, it applies to the Acquirer and Issuer – depending on who wants to request the exemption. EVO is planning to use the TRA exemption and will confirm when this becomes available.
How do I go live with 3DS2?
Note: You may need to enlist the support of your web developer to make these changes.
You may need to make changes to your EVO gateway integration in order to provide the data that is required for 3DS2. To help you with this we are providing you with a list of business scenarios or “use cases.” For each use case we have defined the fields that are required to be sent for authentication. The changes required will vary depending on your integration type and the business scenarios that you support.
For the majority of merchants, the number of mandatory and recommended changes for standard payments are minimal. Details of the use cases and changes can be found below:-
- “If you have an EVO Hosted Payment Page please click here
- If you host your own payment page / form (Direct API) via the Cardstream Gateway, please click here: Integration Guide
- If you have your own payment page / form (Direct API) via a 3rd Party Gateway, please contact them directly and they will provide you with all relevant documentation
Do I have to include all the extra data in the 3DS2 request?
All available data should be provided wherever possible to ensure an optimal cardholder and merchant experience and reduce transaction friction (challenge rate). The more information you include, the greater the chance that the Issuer will not challenge the cardholder with SCA, as it leads to a more informed decision making process.
Will SCA affect conversion rates of my card transactions?
Whilst for the UK the benefit of SCA will be to reduce online card payment fraud levels, it is expected that the changes may also affect conversion rates of people using their card online.
If you do not implement the changes needed to support 3DS2 you will see an increase in declined transactions by card Issuers. As with any new technology, it takes time for cardholders to become familiar with the process and initially SCA may lead to an increased number of abandoned transactions in the short term whilst the number of transactions requiring authentication is expected to decline.
Over time 3DS2 is expected to increase consumer confidence in buying on-line reduce fraud and reduce abandonment rates due to enhanced data flows which is the case in European countries where SCA has been in place for some time now.
How do I find out more?
If you are in any doubt, please contact our support team by emailing ecommercesupport@evopayments.com immediately.
You can read more on SCA and its features on Visa and MasterCard’s websites
Get Started Today
Fill in the form below and a member of our support team will be in touch shortly

